What is Adderall?
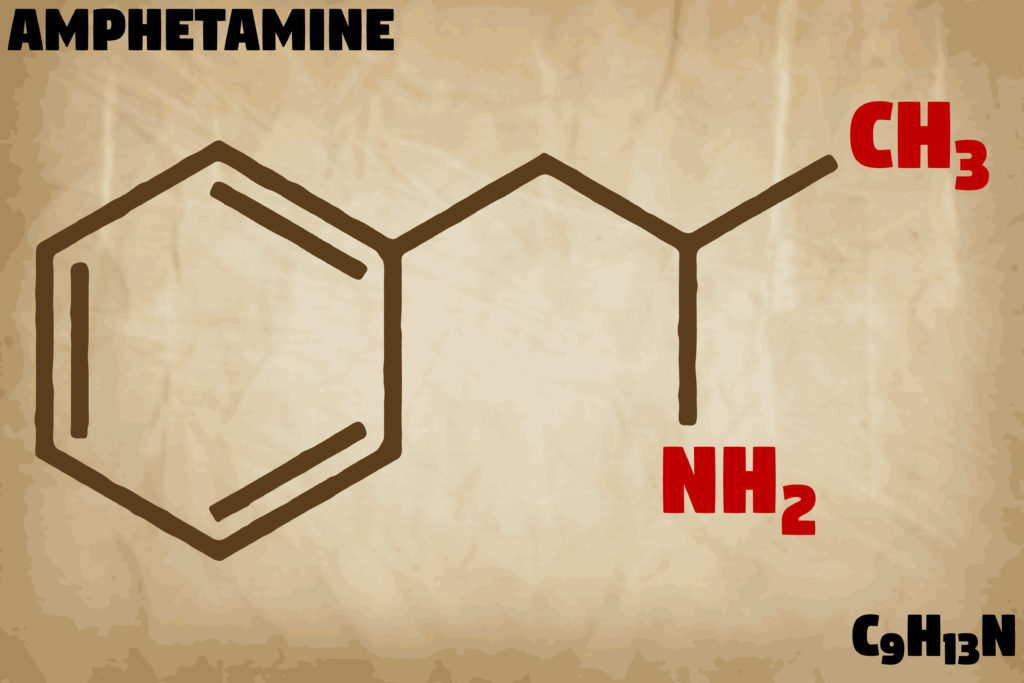
Adderall is a stimulant drug which classifies as an amphetamine. The original form of amphetamines was first synthesized in the late 1880’s by a German chemist. After that, its use grew in the early 1940’s for a majority of countries involved in World War II. The United States military, as well as other international military forces, gave amphetamines to soldiers in battle. The effects of the drugs kept them alert, feeling invincible, and alive during combat.
Through the years, the euphoric effects of amphetamines remain slightly more familiar than the medical effects. It was not until 1996 when Adderall came to the pharmaceutical scene. Adderall became a patent drug comprised of amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, mixed with a combination of salts, processed into a pill form.
As many Americans know, especially in the university or high-pressure business realms of study, Adderall is one of the most commonly-popped pills to this day. Sometimes casually used for even the most innocent straight-A student, there’s likely an Adderal dealer on every dorm floor all across the country.
The effects of Adderall on one person can be different to another. Overall, Adderall and other stimulant drugs like it are widely prescribed to people with a diagnosis for ADD (attention-deficit disorder) or ADHD (attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder). We will learn about how Adderall affects these disorders, but it’s important to know how it affects individuals with normal brain chemistry as well. Specifically, the abuse of this drug occurs among people without a disorder. In fact, Adderall is known as the number one most abused stimulant in the country among young adults.
Common Effects
The effects of Adderall that keep individuals without an attention disorder coming back for more are those that deliver feelings of intense focus, a prolonged boost in energy, euphoria, and often, that feeling of “I am invincible.”
Other common effects on the sensory-level may include:
- Increased heart rate
- Increase in blood pressure
- Euphoria
- A heightened sense of well-being
- Sweating
- Decrease in sleepiness
- Abnormal feelings of greatness
- Feeling a continual sense of being “pumped up”
Who Uses Adderall?
As mentioned above, many college-age students abuse Adderall above anyone else in the country. Also known by its clever term of the “academic steroid,” you or someone you know has probably joked about the apparent much-needed use of Adderall for a long all-nighter or brain-crushing study session. A 2012 study claims that 591 students out of 1,381 students without any mental diagnosis admitted to using Adderall for school or performance-related purposes.
With the increase in dopamine levels that this drug provides, users’ motivation increases and is said to have beneficial effects on the work ethic of the individual. Additionally, the ability for neuroenhancement– although perhaps a myth, maybe even a placebo– seems to be reported as true in most cases of use.
Although these statements have been true in most situations for Adderal misuse and abuse, it is still common for people with ADD or ADHD to abuse this drug, too. Anyone from the ages of young teens to the elderly can misuse, overuse, or harmfully administer Adderall if not properly monitored through the care of their doctor. Depending on how much or how little an individual takes, Adderall can have negative effects on the body and brain. However, if used responsibly, those with ADHD can experience some benefit from their medication.
How Does Adderall Affect the Brain?

Adderall affects the brain much like other amphetamine drugs. When someone takes amphetamine, the brain releases extra dopamine and norepinephrine. It stimulates the central nervous system (CNS). Because of this stimulation, people without an attention disorder experience a heightening in senses and brain function. To someone with an attention deficit disorder (ADD or ADHD), on the other hand, it acts as the opposite. The stimulation of the brain actually causes them to calm down. With this opposite effect, for attention disorders, it is a good thing.
Since people with ADHD have lower levels of dopamine, which is responsible for the brain’s “reward system,” increasing the dopamine levels through low doses of amphetamine drugs help push the dopamine to the proper receptors. This causes the individual to remain stimulated, instead of hyperactive and constantly seeking for outside stimuli to deliver dopamine. They don’t have to bounce from one source of stimulation to another, trying to spike their dopamine levels. Therefore, the increase in dopamine from amphetamines such as Adderall results in the brain’s ability to increase mental focus, concentrate on more detail-oriented tasks, and increase a feeling of calm.
Adderall vs. Meth
You may be wondering if amphetamine drugs include the category of methamphetamines (AKA Meth) as well. The answer is yes– however, the two are quite different and used for completely different things. Meth is a dangerous, illegal drug that is made by dealers in their homes or in the streets. Adderall is processed in a professional medical lab and (hopefully) prescribed by a doctor.
Adderall pills often release slowly into the body so the effects don’t spike too high or cause as much damaging side effects. The once-a-day, slow-release form is known as Adderall RX. Meth, on the other hand, lasts a very short amount of time and it is not regulated at all. It is commonly smoked, snorted, or injected with a needle. Thus, it can be highly addictive as well as dangerous. Drug dealers or “meth labs” that process crystal meth often add harmful chemicals that boost the effects of amphetamine. Added chemicals include household cleaners, battery acid, or even paint thinners. Clearly, this is not up to par with a substance someone would want to take for enhanced cognitive functioning.
How Does Adderall Affect the Body?
Loss of Appetite
One of the most well-known physiological side effects of Adderall is a loss of appetite. Sometimes it is actually prescribed to people as a method of helping treat obesity. Again, as Adderall increases dopamine in the brain, it decreases the craving for dopamine released by food, especially in cases of individuals with food addictions. Another side effect is that it can cause constipation or stomachache in some people.
Increase in heart rate
A rise in heart rate or blood pressure is another common side effect. Because this drug is a stimulant to the central nervous system, this is expected. These symptoms are normal, but if you experience heart palpitations, breathing problems, or chest pain, consult your doctor immediately.
Hives
Hives or a sudden skin rash could occur if you are someone with a rare allergy to Adderall. If you or your loved one experiences this symptom, let your doctor know so you can find another medication, as you could be allergic.
Other symptoms
Other side effects of Adderall include circulation issues. Especially if you or someone you know who is taking Adderall has underlying circulatory conditions, physical symptoms amplified by Adderall include numbness in fingers, coldness in hands or feet, and constricting blood vessels throughout the body.
For those who take or misuse Adderall with no need for a prescription due to ADD or ADHD, a common physical side effect on the body is nervousness or increase in anxiety. Stimulants should not be of interest to someone who suffers from severe anxiety or panic attacks.
Because Adderall increases the norepinephrine (which are the sympathetic nerve fibers that help control skeletal control and muscle control), sleepiness is usually not a side effect. In fact, some doctors give Adderall to patients to help treat narcolepsy. This is also why some people who abuse it say they feel awake for hours on end.
How Long Does Adderall Stay in Your System?
Upon entering the bloodstream, amphetamines such as Adderall can last about four to six hours while feeling the desired effects. Normal Adderall pills may require multiple doses throughout the day for some people according to their doctor. Alternatively, there is a form of Adderall called Adderall XR. This is a slower-releasing pill whose effects can be felt for up to twelve hours. It is important to note with this type, however, that only ONE pill should be taken within 24 hours.
The half-life of Adderall ranges from nine (9) to fourteen (14) hours. Half-life means it takes X amount of hours for half of the original dose of the drug to leave the body. So, in this case, 9 to 14 hours after someone takes the drug, only half the amount of the drug will remain in their system. In order for the drug to completely leave the body, it can take up to three days. In certain instances such as addiction withdrawal or detox, it could possibly take longer to get completely clean.
Regular Adderall vs Extended-Release Adderall
After about two days, the regular immediate-release version of Adderall should be completely clear from the body. In the case of the extended release version– Adderal XR– it could take three to four days.
After two days, regular release most likely will not show results on a urine drug test. However, some other factors might influence the drug reading results. The extended-release could take up to one week to clear a urine drug test. After seven days, it’s most probable that Adderall is completely out of your system. It will then not show results on a urine test.
Some other types of drug tests exist, and the different methods of obtaining results can create different outcomes. For example, a blood test for drugs could show a positive result for Adderall only 12 to 24 hours after the last dose. However, A hair follicle drug screening could detect positive for the drug anywhere from a few days after the last consumption, for up to 90 days. Saliva tests can detect it anywhere from 20 minutes up to two or three days after.
Varying Factors
Although these drug tests carry out similar methods of detection, test results can vary from person to person. Factors for each individual such as weight, body build, diet, the frequency of use, dosage, and health of organ function can have a role in altering the results. It all depends on the person and his or her specific situation.
How is Adderall Addictive?

Since the effects of Adderall begin to wear off at around four or five hours, addictive habits can begin to form if someone trying to use the drug for productivity purposes re-up’s their dose once they start to feel it wear off. Once the brain gets accustomed to receiving so much dopamine, it stops creating more on its own. The more of the substance is present, the less the brain will signal itself to create proper levels regularly. The user may feel a need to constantly take more pills in order to feel the desired effects. Hence, this is why the drug is still considered to be one of the most abused pills in the nation.
ADHD & ADD: ADDerall ADDiction
Even individuals with valid reason to take Adderall for ADD or ADHD can become addicted. Sadly, this is becoming true more and more all around the world. Many teens who take a form of stimulant amphetamine for their attention disorder(s) find themselves relying on the drug for life. Often, they may even have to go through multiple doses of alternative types of medications before they finally settle for one with the least intense side effects. A lot of younger adults with ADHD confess it’s actually, in a way, discouraging for them to see their peers abusing medicines like Adderall. It’s not fun to watch “normal” students get high and completely abuse a drug they, on the other hand, need just to try and maintain a normal focus.
If you or someone you know is showing signs of addiction to Adderall, reach out to one of our professionals. At Prevail Intervention, we uphold quality service to help those struggling with addiction all around the United States. If you need help getting free from drug or alcohol addiction, let us help you find the right rehab center near you. Call our 24/7 Addiction and Mental Health Helpline if you want help answering any questions you may have. We have caring professionals ready to talk with you on the phone and help you through your unique situation. Getting sober and living a healthy life is possible, you just have to be willing to take the first step today.
Related Articles
What is Xanax Addiction?
Peer Pressure and Drug Addiction
How Long Does Oxycodone Stay in Your System?
Intervention Help for Families
Drug Abuse Statistics and Facts
Mental Illness: Intervention and Treatment
What is Klonopin Addiction?
Is Alcohol Considered a Drug?
Top Seven Books About Addiction and Sober Recovery
Top Ten Most Abused Drugs
Sources
Tweaking and Tweeting: Exploring Twitter for Nonmedical Use of Adderall
What Are Prescription Stimulants?
Center for Substance Abuse Research: Amphetamines
